Should You Consider Stocking Up on Zinc?
The mineral known as zinc is critical to build up the body’s defense system, in wound healing processes and cellular division. This aspect closely relates to daily health, and lack of it results in health complications, such as reduced immunity, and slow body healing from diseases. If you are thinking of the usefulness of Zinc and whether its incorporation is something you should do, then keep reading. Learn how to include foods containing zinc or a zinc supplement that will enable you to get the right nutrition.
The Role of Zinc in the Human Body

Zinc is often referred to as a "trace element," meaning the body requires only small amounts of it. However, the functions of zinc are anything but minor. It is involved in over 300 enzyme systems that regulate activities such as cell repair, DNA synthesis, and protein production. Zinc also supports a strong immune system by helping to produce white blood cells that defend the body against pathogens.
Additionally, zinc plays a role in wound healing, taste and smell perception, and growth and development during childhood, adolescence. Without adequate zinc, these essential bodily processes can become compromised, which may lead to a range of health issues.
Zinc and Immune Support
One of zinc's most widely praised benefits is its role in protecting against illness and infection. Research suggests that zinc can help reduce the duration and severity of the common cold by aiding in the production and function of immune system cells, such as T-cells and natural killer cells that fight infections.
Several studies indicated that people with adequate zinc levels may be better equipped to fight off respiratory infections compared to those with deficiencies. While zinc alone is not a cure or guaranteed safeguard for viral infections, it certainly contributes to strengthening the immune system, making it an enticing addition to healthcare routines.
Zinc Deficiency: Are You at Risk?
Many people worldwide don’t get enough zinc in their diets, which can cause symptoms like weakened immunity, delayed wound healing, loss of appetite, and impaired growth in children. Severe deficiency may lead to hair loss, diarrhea, and higher risk of infections.
Those most at risk include vegetarians, older adults, breastfeeding women, and people with conditions that affect zinc absorption, like gastrointestinal diseases. Diets low in animal products, where zinc is most easily absorbed, can also make it harder to meet daily needs.
Monitoring zinc intake is important, especially for at-risk groups. Recognizing deficiency symptoms early and consulting a healthcare provider can help prevent health issues.
Sources of Zinc
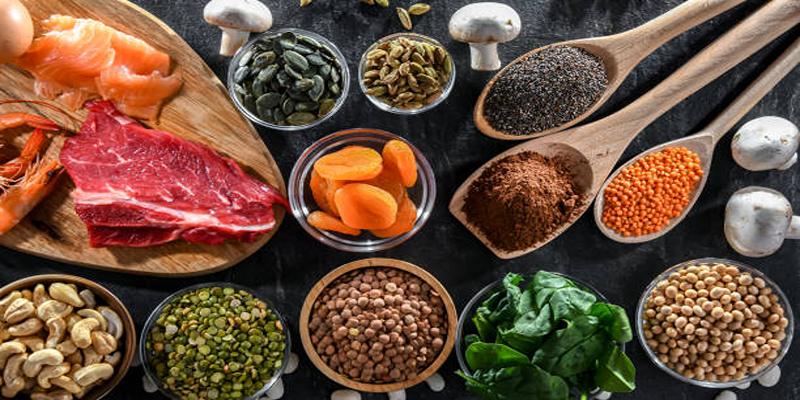
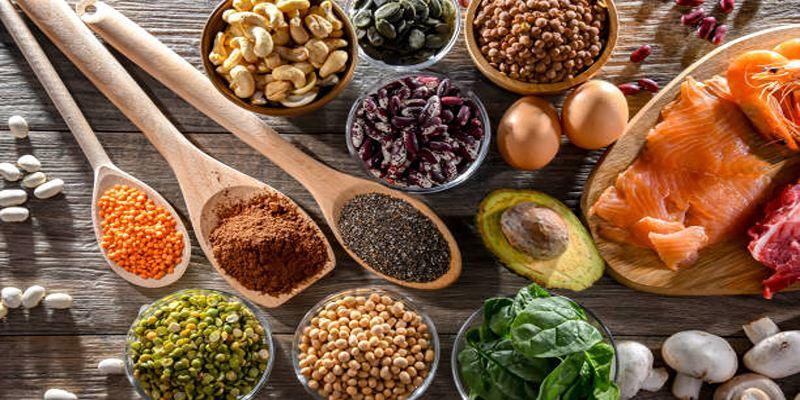
Zinc is naturally present in a variety of foods, but it is more easily absorbed from animal-based sources compared to plant-based ones. Some of the richest dietary sources of zinc include:
- Shellfish: Oysters, crab, and lobster are particularly high in zinc.
- Meat: Beef, pork, lamb, and chicken provide excellent amounts of bioavailable zinc.
- Dairy products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt can contribute to zinc intake.
- Seeds and nuts: Pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, cashews, and almonds offer plant-based options, although absorption from these is lower compared to animal products.
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and beans contain zinc, but their absorption is often hindered by compounds called phytates found in these foods.
- Fortified foods: Breakfast cereals and some grains are fortified with zinc, making them a convenient option for boosting zinc levels.
Including a balanced mix of these foods in your diet is a straightforward way to ensure you're meeting your daily zinc requirements of approximately 11 milligrams for men and 8 milligrams for women.
Should You Supplement with Zinc?
Most people can meet their zinc requirements through a balanced diet, but supplementation may be helpful for those at risk of deficiency. Zinc supplements come in several forms, such as zinc sulfate, zinc gluconate, and zinc acetate, all offering similar levels of bioavailability.
Here are a few circumstances where zinc supplementation might be worth considering:
- Immune Support: If you frequently experience colds or other infections, taking zinc supplements during the early stages of illness may help reduce symptoms faster.
- Vegetarian or Vegan Diets: Plant-based eaters often struggle to obtain sufficient zinc due to the reduced absorption of plant-based zinc sources. A supplement can help bridge the gap.
- Special Health Needs: People with gastrointestinal conditions like Crohn's disease or celiac disease may have difficulty absorbing zinc, making supplementation necessary. Similarly, breastfeeding women may benefit from additional zinc to support their baby's development.
- Recovery Periods: For individuals healing from wounds or recovering from surgery, zinc supplementation may accelerate the healing process.
The Risks of Over-Supplementation
Although zinc is undoubtedly essential, too much of a good thing can be harmful. Consuming zinc in excessive amounts—more than 40 milligrams per day for adults can result in adverse effects such as gastrointestinal distress, reduced immunity, and impaired absorption of other minerals like copper and iron. Chronic overuse of zinc supplements can even cause neurological issues and anemia over time.
To avoid over-supplementation, most experts recommend prioritizing zinc-rich foods first and using supplements only when necessary. Always follow product labeling and consult a healthcare provider before exceeding recommended dosages.
Tips for Incorporating Zinc into Your Lifestyle

Whether you prefer to enhance your zinc intake through food or supplements, here are some practical steps to make zinc a regular part of your health routine:
- Diversify Your Diet: Incorporate a variety of zinc-rich foods like seafood, meat, dairy, and fortified cereals.
- Pair Foods Appropriately: If you rely on plant-based zinc sources, pair them with foods high in vitamin C to improve absorption.
- Rotate Meals: Vary your food choices to ensure a balanced intake of all essential nutrients, including zinc.
- Consult with a Healthcare Provider: If you're considering taking zinc supplements, speak with your doctor or dietitian first to determine the appropriate dosage and form for your needs.
- Be Mindful of Potential Interactions: Zinc can interfere with certain medications, such as antibiotics and diuretics, so it's essential to check for any potential interactions before starting supplementation.
Conclusion
By incorporating zinc into your lifestyle with mindful choices, you can support your overall health and well-being. Whether through a balanced diet rich in zinc or thoughtful supplementation, maintaining adequate levels of this essential mineral is both achievable and beneficial. Remember, consistency is key, and working closely with a healthcare professional ensures your approach is safe and effective. A well-rounded diet complemented by informed decisions will help you enjoy the many advantages zinc has to offer, from boosting immune function to promoting skin health and more. Small, intentional changes can make a big difference in your long-term vitality.