Common Bacterial Infections and Their Effects on Health
Bacteria pose significant health problems for people everywhere around the planet. When harmful bacteria enter our bodies, it produces illness and different symptoms. While many bacterial infections cause simple issues, doctors can take care of others that become dangerous and put your Life at risk. Knowing how bacterial infections differ from viral ones helps medical care succeed because antibiotics work against bacteria only. Early detection of bacterial infections helps medical treatment start before problems arise.

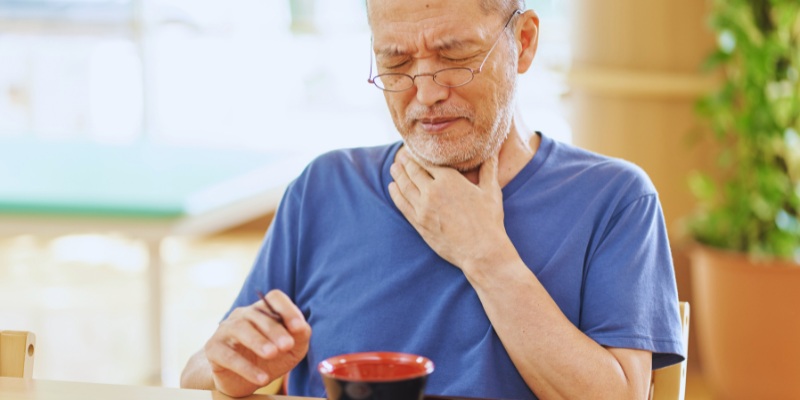
Strep Throat: A Painful Throat Infection
The Streptococcus germs cause the infectious disease known as Strep throat. The bacteria move from one person to another when someone coughs or sneezes. A severe sore throat, swallowing pain, fever, and swollen lymph nodes reveals someone has strep throat. When someone gets a viral sore throat, it makes them cough and run nose, but strep throat does not cause these symptoms. When strep throat stays untreated, serious problems like rheumatic fever or kidney swelling develop. Doctors prescribe antibiotics to treat infections faster and protect others against catching the disease. Sufficient sleep with fluids and throat drops will make your symptoms more manageable.
Urinary Tract Infections: A Common and Painful Issue
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most common bacterial infections affecting the bladder, kidneys, or urethra. They are often caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria, which naturally live in the intestines but can enter the urinary system. Symptoms of a UTI often include a burning feeling during urination, a frequent need to go, urine that appears cloudy or has a strong odor, and pain in the lower abdomen. Women are more prone to UTIs than men due to their shorter urethras. Doctors usually prescribe antibiotics to eliminate the infection, and drinking plenty of fluids helps flush out bacteria. If left untreated, a UTI can lead to kidney infections, which may be more serious.
Pneumonia: A Serious Lung Infection
Bacterial pneumonia happens when Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria attack the lungs to cause an infection. Catching after respiratory infections produces symptoms such as fever spikes, shaking chills, chest discomfort, thick mucus coughing, and breathing trouble. People with weakened immune systems need special care because they face a more significant risk of pneumonia than healthy individuals. Your doctor will prescribe antibiotics, rest, and fluid intake to fight this infection. Medical care at a hospital is necessary when breathing problems develop during this condition. Regular testing and correct medical care help decrease the risk of life-threatening problems such as breathing problems or infection.
Skin Infections: Bacterial Invasions on the Skin
The severity of bacteria-driven skin infections depends on the type of microbes at work. Impetigo produces red sores that commonly develop near the mouth and nose areas. The condition travels from person to person through direct skin touch and affects children most often. Bacterial skin infection cellulitis results in skin that becomes red, swollen, and painful alongside warmth detection at the affected site. Staphylococcus aureus usually appears to be the cause of these infections. Topical antibiotics treat light problems, but oral antibiotics are used in severe cases. To limit bacterial skin infection risks, maintain proper skin hygiene and protect skin from wounds.
Tuberculosis: A Life-Threatening Respiratory Infection
TB develops as a serious bacterial disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The illness primarily strikes the lungs before moving throughout other body parts. An infected person can pass TB through airborne particles released when coughing or sneezing. You might feel a long-lasting cough, chest discomfort, and fever while having heavy night sweats and unexpected weight loss. You need to take many antibiotics over an extended period to cure your TB infection the way you would treat most other bacterial diseases. Treatment failures with tuberculosis can lead to death, which makes early detection an urgent medical need. The world has seen fewer tuberculosis cases through better treatment, improved living spaces, and vaccines, yet fights this disease extensively.
Meningitis: A Dangerous Infection of the Brain and Spinal Cord
Bacterial meningitis attacks the protective layers surrounding your brain and spinal cord, a severe illness that risks your Life. The condition arises from Neisseria meningitidis and Streptococcus pneumoniae bacterial infections. The infection shows quick signs of severe headache, fever, neck pain, stomach issues, and light sensitivity. Getting medical help right away becomes critical because untreated bacterial meningitis causes brain damage and hearing loss or ends in death. Patients require hospital care plus antibiotics through an IV line to fight their infection. Vaccine protection works well to free users from certain types of bacterial meningitis.

Gonorrhea: A Common Sexually Transmitted Infection
Gonorrhea is a bacterial infection caused by the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium, and it spreads through sexual contact. It affects both men and women, primarily infecting the genitals, throat, or rectum. Many people with gonorrhea do not experience symptoms, but when symptoms occur, they may include painful urination, abnormal discharge, and pelvic pain. If left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to serious complications such as infertility or an increased risk of other infections. Antibiotic treatment is necessary to eliminate the bacteria, and regular screening helps detect the disease early. Safe sexual practices can reduce the risk of transmission.
Food Poisoning: A Bacterial Threat from Contaminated Food
Food becomes toxic when harmful bacteria, including Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria, enter your food. The main signs you may experience when food is infected with bacteria include feeling sick to your stomach, throwing up, having loose bowel movements, suffering abdominal pain, and having temperature spikes. Bacterial infections target multiple body parts that need antibiotic treatment to heal. To diagnose conditions correctly, you need to know which infections come from germs versus viruses. Proper hygiene alongside safe habits combined with vaccinations keep infections under control. Getting updates on disease risk helps people take early action to keep themselves safe.